Baking a Java EE 8 Micro Pi
 This talk by Payara guys Ondrej Mihalyi and Mike Croft debunked the myth that Java EE is heavy.
This talk by Payara guys Ondrej Mihalyi and Mike Croft debunked the myth that Java EE is heavy.
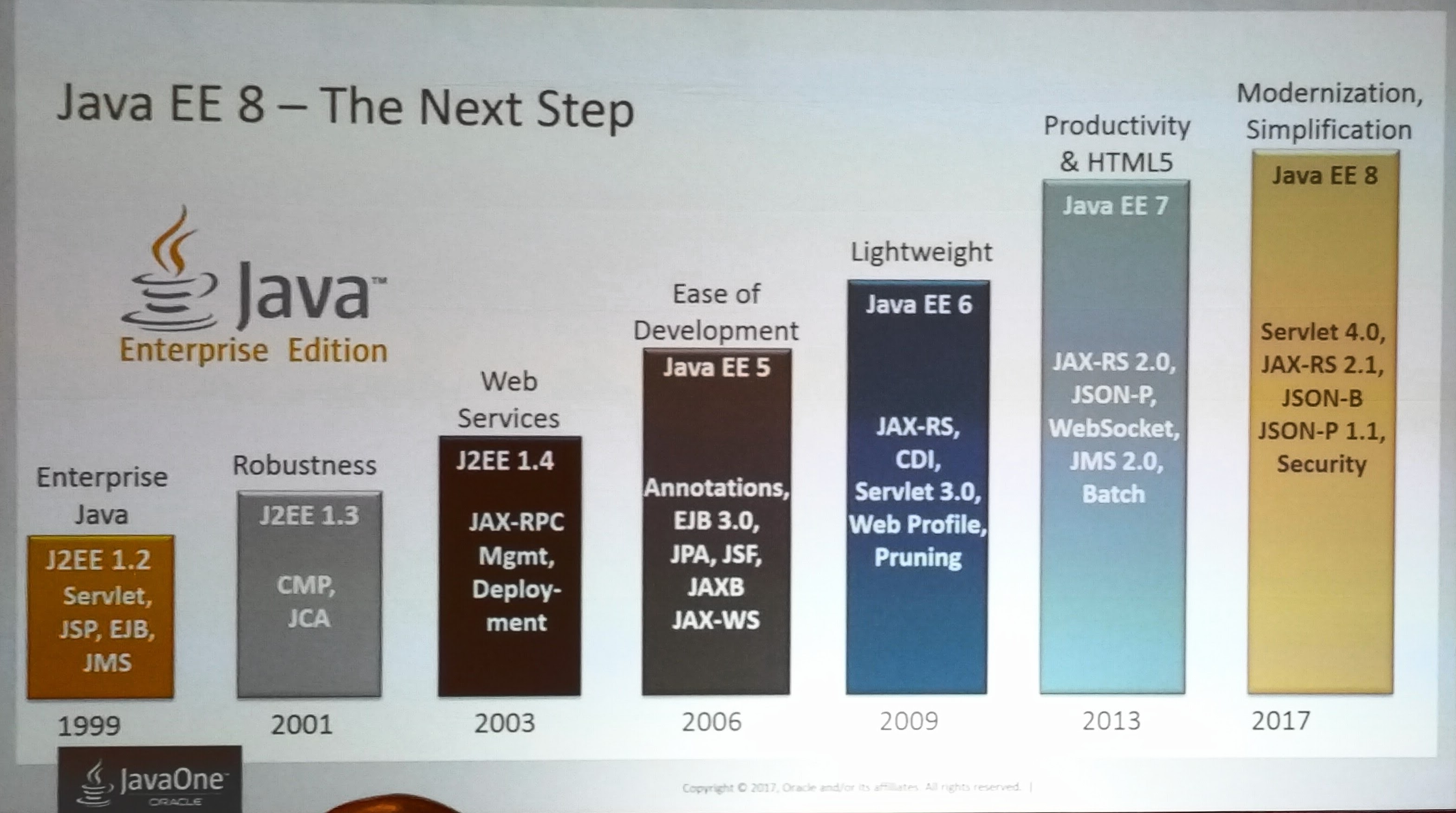
Some recent history (to put things into perspective):
2013 Java EE 7 was released (4 years ago)
- Docker was only 3 months old
- Wildfly was still called JbossAS
- Wildfly Swarm did not exist (publicly)
- SpringBoot was not yet released
- WebSphere Liberty was just released
2017 Java EE 8 released
- Docker is the dominant container
- Wildfly productionize Swarm
- SpringBoot started the “fat jar” movement
- IBM OpenSourced Liberty
- Payara entered the market, including Payara Micro
- Eclipse Microprofile released 1.2 with some new APIs
- Configuration API
- Metrix and health check
- JWT
They then discussed all the new features in Java EE 8 (See next talk for more details)
Unfortunately, due to technical issues (not from the speakers), they could not do the demo. (I did go down to their booth to see it though). So we went through the code rather.
Some nice (Payara specific) features:
@Clusteredwill make a Bean Cluster aware@Outboundannotation- Remote/Clustered CDI Events
- Clustered Config (based on Hazelcast)
Some prediction on the future of Java EE - “Look at Microprofile”
Java EE 8: What’s New in the Java EE 8 Release
Linda DeMichiel is the spec lead for Java EE and part of many other specs. She gave a high level overview of new features in Java EE 8, that was focus on:
- Ease of use
- CDI
- Modern security
- HTTP2 support
The release of the specification was delayed due to a 1 year hiatus, where some of the spec leads got moved to some internal Oracle work. With the move to Eclipse (EE4J) this should not happen again.
JSON-P
Support added for emerging IETF standards:
- JSON Router - Kind of like XPath (but more) for Json, allowing you to manipulate (add,remove,replace) parts in a JSON document using a path-like structure.
- JSON Patch - A piece of Json Document itself that you can patch another document with. You can add, copy, move, remove and replace a part of a document.
- JSON Merge Patch - Kind of like git merge (I think)
Also added support for JSON Collections
JSonArray contacts = ...;
List<String> femaleNames =
contacts.getValueAs(JSonObject.class).stream()
.filter(x->"F".equals(x.getString("gender")))
.map(x->(x.getString("name")))
.collect(Collections.toList());
JSON-B
- New API (Basically JAXB for JSON).
- You can also (like JAXB) write your own custom mappings.
- You can hook in one of the existing JSON-Object mappers:
Builder.newBuilder("provider")
JAX-RS 2.1
Updated with the following:
- Reactive client API
- Server Side Events (HTML5 standard)
- Support for JSON-P
- Support for HTTP Patch
- Client can also subscribe to SSE
The RX client changes the way you do Async in a REST client (much less verbose)
WebTarget target = client.target("http://com.example/service/subscribe");
try(SseEventSource eventSource =
SseEventSource.target(target).build()){
eventSource.register(System.out::println);
eventSource.open();
}catch(InteruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
Servlet 4.0
HTTP2 Support that resulted in:
- Reduced latency
- Parallelism (performance improvement)
- Header compression
(More on this in the next talk)
JSF 2.3
- Better CDI integration
- WebSockets Support
- Class level Bean validation
- New Java Date Time API Support
CDI 2.0
The Spec split into 3 parts:
- core
- standard edition
- enterprise edition
This means you can now use CDI in plain Java SE.
Some new features:
@Observerordering with@Priority- Async event firing and listening with
@ObserverAsync - Built-in annotation filters (ease of use)
- New Java 8 Stuff (like Streams)
- CDI SPI
Bean validation 2.0
- New Java Data time support
- Repeatable annotations
- Constraints with container elements
- Optional support
- More Built-in Constraints added (eg
@Email)
@Past
Year startYear = Year.of(2016)
@Size(min = 8, group = Default.class)
@Size(min = 12, group = Admin.class)
private String password;
New (simplified) Security API
- Security Context (based on JASPIC)
authenticate()getCallerPrinciple()getCallerPrincipleByType()
- HTTPAuthenticationMechanism
- Intended for Servlet container use
validateRequest()secureResponse()cleanSubject()
- Identity store
- To interact with user stores (LDAP, Database, Embedded)
- You can provide your own store
- You can chain stores
The future of Java EE
She then discussed the future of Java EE. More on that later in another talk.
Servlet 4.0: A New Twist on an Old Favorite

Servlet 4.0 Spec leads Ed Burns and Shing wai Chan went into detail on the new HTTP2 support in Servlet 4.0.
HTTP2 gives us:
- Binary framing
- Stream multiplexing
- Header compression (HPACK)
- Server push (RFC7540)
- HTTP Trailer (RFC7230 and RFC7540)
Servlet 4:
- You can now respond to requests in multiple resources and in parts.
- The same header is a full text initially, and then just an int.
- You can turn server push on and off. This means that when using
PushBuilderyou need to check for null. - You can add Meta data to the end of the request and response body. This is useful for checksum, digital signatures and GRPC
Another new cool feature, Mapping discovery, allows you to discover how the current servlet was reached.
Java Keynote

This keynote actually deserves a blog post on it’s own. You can see the video here
Some of my notes:
- Intel showed Persistent Collections for Java
- and Distributed Deep Learning Library for Apache Spark
- Spotify started with Python but moved to Java to scale. They are doing 4 million requests per second (think about that)
- Oracle showed Wercker - Build, deploy and operate container-native applications at scale
- and said, going forward, there will be zero difference in openJDK and Oracle JDK
- they also heavily invest in Kubernetes
- Oracle announced and open sourced FN(https://blogs.oracle.com/developers/announcing-fn) - An Open Source Serverless Functions Platform
- RedHat, IBM, Oracle and Tomitribe discussed the Java EE move to Eclipse.
- Mark Reinhold showed some features of the recently release Java 9.

Java changed more in the last 3 week than in the last 13 years
Opening Up Java EE: Panel Discussion with Oracle, IBM, Red Hat, and the Eclipse Foundation

Discussion Panel:
This panel discussed the recently announced open sourcing of Java EE and the move to the eclispe foundation, and the renaming to EE4J.
The Eclipse foundation, with all the vendors, will:
- Host and maintain the reference implementation
- Host and maintain the TCK
- Host the documentation
In the future we might see Microprofile be included in this project.
The goal is to make EE4J more Nimble, Agile, Flexible, Compatible and Vendor neutral.
Because the TCK is now accessible to everyone, we might see more implementations. Previously the TCK was a control point (“Pay to play”). Open sourcing it changes the dynamics.
Community involvement matters ! “Resist the urge to wait and see” - David Blevins
The eclipse foundation is funded by it’s members. see https://www.eclipse.org/membership/exploreMembership.php#allmembers

“I don’t care about the name of the band, I care about the music” - David Blevins on the name change.
When Should You Look at GraphQL as an Alternative to REST APIs?
Jobinesh Purushothaman, a published author on REST, discussed GraphQL and when you might want to look at using that rather than REST.
Initially we had RMI, then EJB then JAX-WS now JAX-RS. What is next ?
With REST a client sometimes needs to make multiple calls to get what he/she wants. Example:
GET /departmentsGET /departments/employeesGET /departments/employees/10
You need to explicitly document your REST API with Swagger, OpenAPI or
To control the payload in REST, you typically add query parameters that allow the called to specify what it is looking for, or the client just gets everything and has to filter himself.
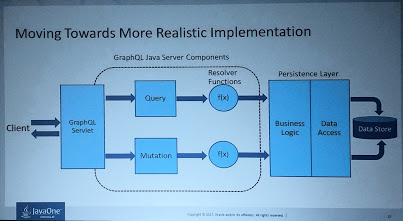
GraphQL is a query language for your API, built by Facebook. (It’s got nothing to do with Graph databases)
It’s self documenting and allows the client to query only what he/she is interested in, in one call. Not more over and/or under fetching. Versioning is also not needed when using GraphQL.
Some Java libraries that enable this can be found here: https://github.com/graphql-java Some client side libraries (Android, JavaScript etc) can be found here:https://github.com/apollographql
We need to seriously look at this !
JCP Party !

I then went to the JCP Party on the 38th floor of the Marriott Hotel, where the winners of Duke’s choice awards and JCP Awards were announced. I also got a change to chat to many community leaders and Spec leads.